Recovering / reinstalling SRM (Site Recovery Manager) 4.1.1 after suffering a host failure
I’ve been meaning to write a post about recovering / reinstalling SRM 4.1 after having to rebuild one when a client suffered a host failure but never got the chance to until this weekend. The incident happened during a planned datacenter move a few weeks ago where the environment had SRM 4.1 collocated with vCenter 4.1 on a physical server and someone decided to perform firmware upgrades during the move which resulted in the vCenter server continuously bluescreen-ing after the upgrade. The priority during that when the host failed was obviously not the recovery of SRM because vCenter was more important but I ended up going in to recover SRM a few days later. What I noticed as I started the recovery was that I wasn’t able to find a public KB from VMware that clearly outlined steps for situations such as these and the closest KB article I was able to find was the:
Migrating an SRM server to run on a different host
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1008426
So armed with this KB, I went on reinstall SRM 4.1 onto the production vCenter 4.1 server (the protected site).
Assumptions
The following are the assumptions for the environment:
- There have been no changes made to the SAN replication and it is still in working order.
- You are using the same vCenter version prior to the failure.
- You have a backup of the SRM database.
- SRM is using Microsoft SQL server for the database service.
Downloading the SRA (Storage Replicator Adapters)
Before proceeding to reinstall SRMs, you should download the SRA for the SAN so proceed with opening up a web browser and navigate to:http://www.vmware.com/download/srm:
Click on the Show Details link to expand the list of downloads:
Proceed with scrolling down the list of downloads to the one for your SAN:
Download and install Microsoft SQL server for SRM 4.1
The next step for the recovery process is to install Microsoft SQL and I can’t help but to vent that I’ve come across way too many environments with the incorrect Microsoft SQL server installed. While I have yet to see an install cease to function because an unsupported Microsoft SQL server was used, I still prefer to stick with what VMware has listed in the SRM Compatibility Matrix 4.x (srm_compat_matrix_4_x.pdf) so please refer to the following list for the support SQL Server editions:
For the purpose of this demonstration, I will be using SQL Server 2005 Express Edition SP2 which can be downloaded here:
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=22625
Proceed with the install by running the executable:
Configuring Microsoft SQL Server for SRM
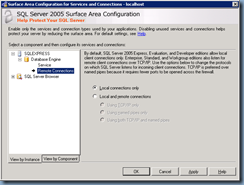
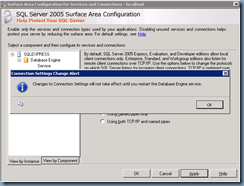
Once SQL server has been installed, open the SQL Server 2005 Surface Area Configuration for the instance:
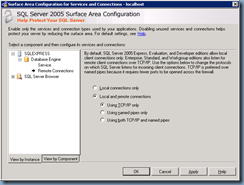
Navigate to Instance Name –> Database Engine –> Remote Connections and change Local connections only to Local and remote connections with the option Using TCP/IP only:
Clicking on the Apply button will prompt you with a warning message that the changes will not apply until you restart the database services but you won’t need to restart the services just yet as there are still changes required to be made:
Proceed with opening SQL Server Configuration Manager and navigate to SQLServer 2005 Network Configuration (32bit) –> Protocols for SQLEXPRESSand enable TCP/IP:
You will again be prompted with a warning that you will need to restart the services for the changes to take effect but there are still change required to be made for a restart so proceed with the next steps:
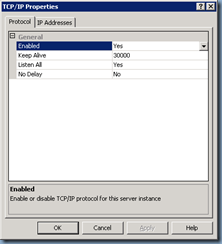
If you’re using SQL Server Express as shown in this demonstration, you will need to remove the dynamic ports that the default installation sets so open SQL Server Configuration Manager and navigate to SQL Server 2005 Network Configuration (32bit) –> Protocols for SQLEXPRESS right click on TCP/IPand choose Properties:
Navigate to the IP Addresses tab and make sure you change all of the TCP Portto 1433 (default for Microsoft SQL) and TCP Dynamic Ports to the value of 0:
Applying the changes will once again warn you that a service restart will be required for the changes to take affect but we’re not done with the changes so proceed on with the next steps:
There is no need for Shared Memory, Named Pipes or VIA to enabled so disable the protocols if they’re still enabled:
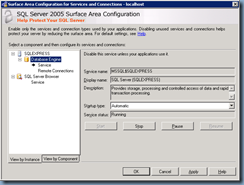
With all of these changes made, proceed with restarting the services either in the service console:
… or the SQL Server 205 Surface Area Configuration:
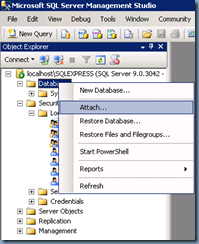
Restoring SRM Database
Proceed with launching the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studioadministration console:
From here, you have the options of:
- Restore an .bak file of your SRM database from a previous backup.
- Re-attach the .mdf and .ldf files for your SRM database.
In my situation, the client had the .mdf and .ldf files stored on a separate LUN so all I had to do was reattach the LUN to the server and reattach the database. With that being said, if you don’t intend on restoring the master database to this SQL Express server such as what I’m doing here, the security logins for the server will be missing so prior to reattaching or restoring the database, you will need to configure the security account used for the DSN connection on the SQL server instance first.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
If you’re going to restore the master database, you can ignore the following step:
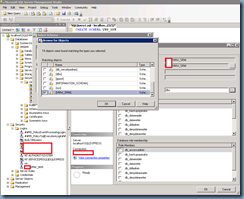
Navigate to localhost\SQLEXPRESS –> Security then right click on Logins and select New Login. Within the Login – New window, select the account you used to connect to the SRM database prior to the reinstall:
Once you’ve added the login configured, proceed with clicking the OK button and confirm that the login is now listed under the Logins node:
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
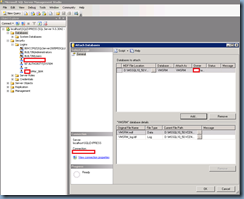
With the service account created under the SQL Express database’s login, proceed with restoring your SRM database. The following demonstration will use the Attach feature:
With the database restored, we will now proceed with configuring the other requirements required for the SRM database outlined in the deployment guide:
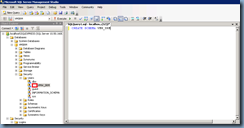
Open up a new SQL query and execute the following command:
CREATE SCHEMA VMW_SRM
Note that VMW_SRM is the database in this demonstration and is not a requirement to be named that way.
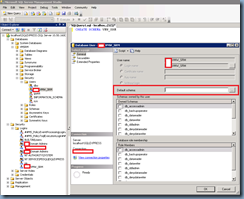
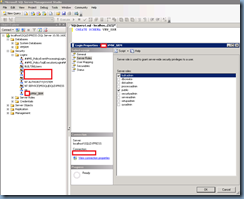
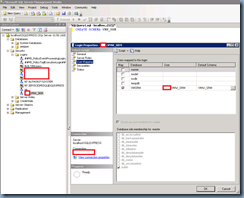
With the schema with the same name as the service account used for the DSN accessing the database created, open up the SRM database’s properties and configure the Default schema with the schema we created:
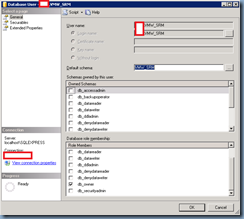
With the databases’ configuration complete, proceed with opening the properties of the service account you’re using for the DSN connection and give itbulkadmin and public roles:
Map the account to the SRM database:
Configuring the 32-bit SRM DSN
With the configuration for the database and user account completed, proceed with creating the 32-bit DSN for the SRM database. I won’t go into too much detail but for more information, please refer to one of my vCenter / Update Manager posts (use the 32-bit instructions):
http://terenceluk.blogspot.com/2011/02/creating-vcenter-update-manager-41-sql.html
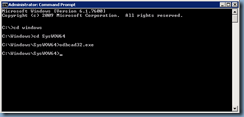
cd\Windows\syswow64
odbcad32.exe
Installing SRM 4.1
Now that all of the prerequisites have been installed and configured, proceed with running the installation binaries for VMware Site Recovery Manager:
Note that you’ll be warned that your production vCenter server already has an extension registered for SRM during the vCenter server registration section and since you’re recovering from a host failure, proceed with selecting Yes:
Note that it is important that you fill in the field Local Site Name with the same site name you used for the SRM site you are recovering or you’ll receive the an error when you’ve completed the recovery:
Make sure you select the Use existing database option:
Reinstalling the SRA (Storage Replicator Adapters)
With SRM reinstalled, proceed with installing the SRA you downloaded earlier:
Download and install vCenter Site Recovery Manager
With the SRA installed, proceed with launching vCenter and install the vCenter Site Recovery Manager plug-in:
Launch Site Recovery Manager
With the plug-in for SRM installed and enabled, proceed with opening the Site Recovery plug-in:
Run the installcreds utility to register account credentials on the new host with the old DSN
Open up the command prompt as an administrator and change the directory to:
C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager\bin>
… within the directory above, execute the following:
installcreds.exe -key db:srm -u domain\vmw_srm
For this demonstration, the database user name is a domain account named VMW_SRM so please change that to the appropriate domain and user account for your environment.
Run the srm-config utility to establish an authenticated connection to the local VirtualCenter server
Open up the command prompt as an administrator and change the directory to:
C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager\bin>
… within the directory above, execute the following:
srm-config.exe -cmd updateuser -cfg ..\config\vmware-dr.xml -u VMW_SRM
For this demonstration, the database user name is VMW_SRM so please change that to the appropriate user account for your environment.
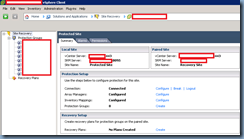
Review Protection Groups
Proceed with logging into the Site Recovery plug-in and verify that your protection groups are in good health:
… and we’re done! I ran into more errors after bringing the protected site up but will separate those errors into other blog posts instead.